Understanding the Endocannabinoid System: A Comprehensive Guide
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex and vital human body component, playing a crucial role in regulating many physiological processes. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the ECS, shedding light on its functions, components, and impact on overall health and well-being. Often referred to as a bridge between body and mind, the ECS helps maintain homeostasis, balancing the body’s internal environment in response to external changes. As we explore the realms of this remarkable system, we uncover how it interacts with various biological pathways and its significance in understanding modern medical sciences.
The Components of the Endocannabinoid System
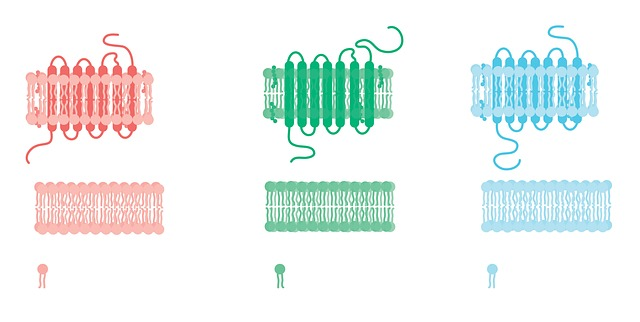
The endocannabinoid system comprises three core components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes. Endocannabinoids, similar to cannabinoids found in cannabis, are naturally produced by the body and play a pivotal role in internal stability. These molecules bind to cannabinoid receptors, which are dispersed throughout the body. The two primary receptors, CB1 and CB2, are found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They respond to various stimuli, influencing pain sensation, mood, appetite, and memory. Enzymes in this system, mainly fatty acid amide hydrolase and monoacylglycerol lipase, break down endocannabinoids once they’ve fulfilled their function, ensuring equilibrium within the ECS.
The Functioning of the Endocannabinoid System
The functioning of the ECS is integral to maintaining homeostasis in the body. It achieves this through a series of complex interactions and responses. When an imbalance is detected, the body synthesizes endocannabinoids, which travel to the appropriate receptors to signal a need for action. For instance, if an individual is experiencing stress, endocannabinoids might target CB1 receptors in the brain to help regulate mood. The unique aspect of the ECS is its precise and targeted response, ensuring that it acts only where and when necessary. This precision is critical in the system’s ability to maintain balance across various physiological conditions.
Evolution and Research of the Endocannabinoid System
The discovery and understanding of the endocannabinoid system have evolved significantly over the years. Initially, research in this area was primarily driven by an interest in understanding how cannabis exerts its effects on the body. This exploration led to the groundbreaking discovery of the ECS in the late 20th century. Since then, the ECS has been the subject of extensive scientific study, revealing its profound impact on human health. Current research continues to uncover how this system influences everything from stress response and sleep patterns to immune system function and pain management. As research progresses, the potential therapeutic applications of targeting the ECS continue to expand, opening new avenues in medical science.
The Endocannabinoid System and Its Relation to CBD Products
In recent years, the intersection of the endocannabinoid system with CBD (cannabidiol) products has garnered significant attention. CBD, a non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis, interacts with the ECS, but not in the same way as typical cannabinoids like THC. Unlike THC, CBD does not bind directly to the cannabinoid receptors. Instead, it influences the system indirectly, which may explain its reported therapeutic benefits without the psychoactive effects associated with THC. This interaction has sparked a surge in CBD product usage for various health and wellness purposes. However, it’s important to note that while CBD products can influence the ECS, they are not a cure-all and should be considered part of a broader health regimen.
The Endocannabinoid System and Homeostasis
One of the most critical functions of the endocannabinoid system is its role in maintaining homeostasis. Homeostasis refers to the body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external fluctuations. The ECS achieves this by subtly influencing various physiological processes. For example, it can regulate body temperature, control inflammatory responses, and manage energy expenditure. By fine-tuning these processes, the ECS ensures that the body operates within optimal parameters, promoting overall health and well-being. This intricate balancing act highlights the system’s importance as a key player in the body’s internal regulation mechanisms.
Future Directions in Endocannabinoid System Research
The exploration of the endocannabinoid system is still in its nascent stages, with many avenues for future research. Scientists are actively investigating how variations in the ECS may contribute to different health conditions and how this system can be targeted for therapeutic interventions. Moreover, there is a growing interest in the potential of cannabinoids and their analogs in treating a variety of disorders. As our understanding of the ECS expands, it promises to unveil new possibilities in the realm of medicine, offering hope for more effective treatments for a range of diseases and conditions.
Conclusion of “What is the endocannabinoid system?”
In conclusion, the endocannabinoid system is a fundamental and dynamic component of human physiology, essential for maintaining homeostasis. Its intricate network of receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes is pivotal in regulating many bodily functions, from pain perception to immune responses. The ongoing research into the ECS deepens our understanding of how our bodies maintain balance and opens new doors in medical science, particularly in relation to CBD products. As we continue to explore this complex system, it stands as a testament to the sophisticated nature of the human body and its capacity for self-regulation.
Frequently Asked Questions Related to the endocannabinoid system.
Q: What is the endocannabinoid system (ECS)?
A: The endocannabinoid system is a complex network in the body that helps maintain homeostasis by regulating various physiological processes through its components – endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes.
Q: How does the endocannabinoid system interact with CBD products?
A: CBD products interact with the ECS indirectly, influencing its functioning, which may contribute to their therapeutic benefits without the psychoactive effects associated with THC.
Q: What are the future research directions for the endocannabinoid system?
A: Future research is focused on understanding how variations in the ECS contribute to different health conditions and exploring the potential of cannabinoids for therapeutic interventions.